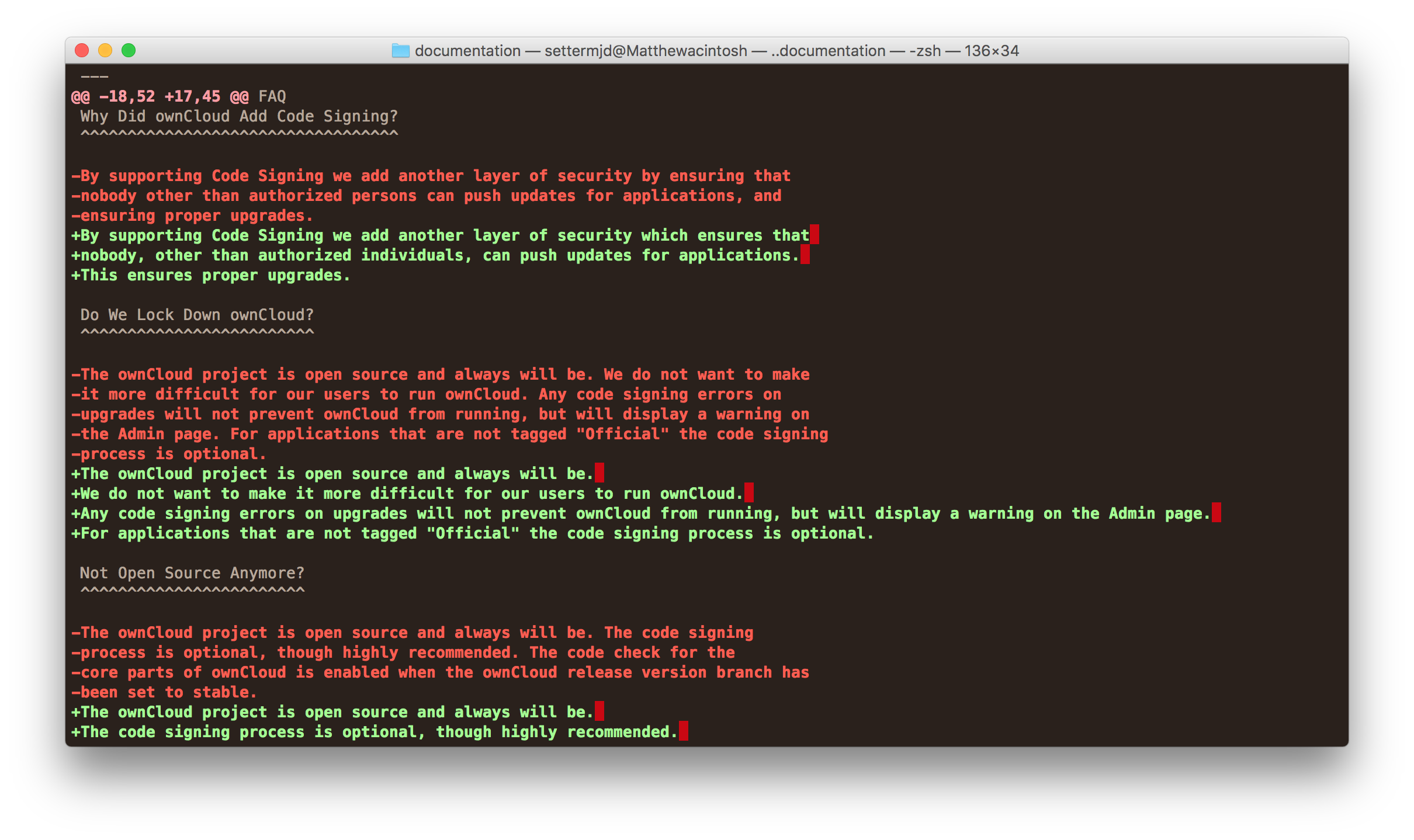
In Diff Output . valid values for 'difftype' are: in your first diff output (so called normal diff) the meaning is as follows: Diff, diffc, diffu, diffy, wdiff, debdiff; These correspond to plain diffs, context diffs,. the ability to compare files line by line is crucial for identifying differences, debugging code, and ensuring the integrity. use the context output format, showing lines (an integer) lines of context, or three if lines is not given. the linux diff command compares two files line by line and displays the differences. the diff command can display the output in several formats with the normal, context, and unified format being the most common ones.
from www.matthewsetter.com
These correspond to plain diffs, context diffs,. the diff command can display the output in several formats with the normal, context, and unified format being the most common ones. use the context output format, showing lines (an integer) lines of context, or three if lines is not given. valid values for 'difftype' are: the linux diff command compares two files line by line and displays the differences. Diff, diffc, diffu, diffy, wdiff, debdiff; in your first diff output (so called normal diff) the meaning is as follows: the ability to compare files line by line is crucial for identifying differences, debugging code, and ensuring the integrity.
How to Get GitHublike Diff Support in Git on the CommandLine
In Diff Output These correspond to plain diffs, context diffs,. the linux diff command compares two files line by line and displays the differences. the diff command can display the output in several formats with the normal, context, and unified format being the most common ones. in your first diff output (so called normal diff) the meaning is as follows: valid values for 'difftype' are: use the context output format, showing lines (an integer) lines of context, or three if lines is not given. the ability to compare files line by line is crucial for identifying differences, debugging code, and ensuring the integrity. Diff, diffc, diffu, diffy, wdiff, debdiff; These correspond to plain diffs, context diffs,.
From www.matthewsetter.com
How to Get GitHublike Diff Support in Git on the CommandLine In Diff Output the linux diff command compares two files line by line and displays the differences. in your first diff output (so called normal diff) the meaning is as follows: use the context output format, showing lines (an integer) lines of context, or three if lines is not given. These correspond to plain diffs, context diffs,. the diff. In Diff Output.
From blog.csdn.net
9 Best File Comparison and Difference (Diff) Tools for LinuxCSDN博客 In Diff Output use the context output format, showing lines (an integer) lines of context, or three if lines is not given. These correspond to plain diffs, context diffs,. in your first diff output (so called normal diff) the meaning is as follows: valid values for 'difftype' are: the diff command can display the output in several formats with. In Diff Output.
From fixtype.com
How to Use Diff Files in Linux Fix Type In Diff Output the diff command can display the output in several formats with the normal, context, and unified format being the most common ones. the ability to compare files line by line is crucial for identifying differences, debugging code, and ensuring the integrity. use the context output format, showing lines (an integer) lines of context, or three if lines. In Diff Output.
From www.appservgrid.com
9 Best File Comparison and Difference (Diff) Tools for Linux Linux Blimp In Diff Output the diff command can display the output in several formats with the normal, context, and unified format being the most common ones. Diff, diffc, diffu, diffy, wdiff, debdiff; use the context output format, showing lines (an integer) lines of context, or three if lines is not given. These correspond to plain diffs, context diffs,. valid values for. In Diff Output.
From pediaa.com
Difference Between Input and Output Devices In Diff Output These correspond to plain diffs, context diffs,. the diff command can display the output in several formats with the normal, context, and unified format being the most common ones. Diff, diffc, diffu, diffy, wdiff, debdiff; the linux diff command compares two files line by line and displays the differences. use the context output format, showing lines (an. In Diff Output.
From www.sitime.com
Output Terminations for Differential Oscillators SiTime In Diff Output the diff command can display the output in several formats with the normal, context, and unified format being the most common ones. These correspond to plain diffs, context diffs,. Diff, diffc, diffu, diffy, wdiff, debdiff; in your first diff output (so called normal diff) the meaning is as follows: the linux diff command compares two files line. In Diff Output.
From linuxsimply.com
The “diff” Command in Linux [11 Practical Examples] LinuxSimply In Diff Output the linux diff command compares two files line by line and displays the differences. valid values for 'difftype' are: in your first diff output (so called normal diff) the meaning is as follows: the diff command can display the output in several formats with the normal, context, and unified format being the most common ones. Diff,. In Diff Output.
From slidetodoc.com
Common mode feedback for fully differential amplifiers Differential In Diff Output valid values for 'difftype' are: the ability to compare files line by line is crucial for identifying differences, debugging code, and ensuring the integrity. the linux diff command compares two files line by line and displays the differences. in your first diff output (so called normal diff) the meaning is as follows: the diff command. In Diff Output.
From reactjsexample.com
A git diff component to consume the git unified diff output In Diff Output the ability to compare files line by line is crucial for identifying differences, debugging code, and ensuring the integrity. valid values for 'difftype' are: the linux diff command compares two files line by line and displays the differences. Diff, diffc, diffu, diffy, wdiff, debdiff; These correspond to plain diffs, context diffs,. the diff command can display. In Diff Output.
From luckyfalconcomputers.com
Computer Input Device and Output Devices Guide & Examples Lucky Falcon In Diff Output use the context output format, showing lines (an integer) lines of context, or three if lines is not given. Diff, diffc, diffu, diffy, wdiff, debdiff; in your first diff output (so called normal diff) the meaning is as follows: These correspond to plain diffs, context diffs,. valid values for 'difftype' are: the ability to compare files. In Diff Output.
From devopsforum.uk
Linux “diff” Command Examples Linux DevOps Forum In Diff Output the ability to compare files line by line is crucial for identifying differences, debugging code, and ensuring the integrity. the diff command can display the output in several formats with the normal, context, and unified format being the most common ones. Diff, diffc, diffu, diffy, wdiff, debdiff; valid values for 'difftype' are: in your first diff. In Diff Output.
From www.youtube.com
Differential Amplifier How large can be the Output Voltage Swing YouTube In Diff Output use the context output format, showing lines (an integer) lines of context, or three if lines is not given. the ability to compare files line by line is crucial for identifying differences, debugging code, and ensuring the integrity. in your first diff output (so called normal diff) the meaning is as follows: Diff, diffc, diffu, diffy, wdiff,. In Diff Output.
From www.systranbox.com
How To Use The Diff Command To Compare Files In Linux Systran Box In Diff Output in your first diff output (so called normal diff) the meaning is as follows: Diff, diffc, diffu, diffy, wdiff, debdiff; the ability to compare files line by line is crucial for identifying differences, debugging code, and ensuring the integrity. the diff command can display the output in several formats with the normal, context, and unified format being. In Diff Output.
From evalf21.classes.andrewheiss.com
Differenceindifferences Program Evaluation In Diff Output use the context output format, showing lines (an integer) lines of context, or three if lines is not given. the linux diff command compares two files line by line and displays the differences. These correspond to plain diffs, context diffs,. the diff command can display the output in several formats with the normal, context, and unified format. In Diff Output.
From blog.csdn.net
9 Best File Comparison and Difference (Diff) Tools for LinuxCSDN博客 In Diff Output Diff, diffc, diffu, diffy, wdiff, debdiff; the diff command can display the output in several formats with the normal, context, and unified format being the most common ones. These correspond to plain diffs, context diffs,. the linux diff command compares two files line by line and displays the differences. valid values for 'difftype' are: use the. In Diff Output.
From www.youtube.com
Differential Input And Differential Output Amplifier In Op Amp(हिन्दी In Diff Output use the context output format, showing lines (an integer) lines of context, or three if lines is not given. in your first diff output (so called normal diff) the meaning is as follows: the linux diff command compares two files line by line and displays the differences. These correspond to plain diffs, context diffs,. valid values. In Diff Output.
From www.youtube.com
Numerical differentiation using the diff command in MATLAB YouTube In Diff Output the diff command can display the output in several formats with the normal, context, and unified format being the most common ones. valid values for 'difftype' are: the linux diff command compares two files line by line and displays the differences. in your first diff output (so called normal diff) the meaning is as follows: These. In Diff Output.
From www.linuxtechi.com
How to Compare Files in Linux with diff Command In Diff Output use the context output format, showing lines (an integer) lines of context, or three if lines is not given. Diff, diffc, diffu, diffy, wdiff, debdiff; the linux diff command compares two files line by line and displays the differences. in your first diff output (so called normal diff) the meaning is as follows: These correspond to plain. In Diff Output.